It’s been practically a century since Alexander Fleming revolutionized trendy medication along with his discovery of penicillin. Since then, antibiotics have saved tens of millions of lives world wide. In reality, analysis suggests Fleming’s breakthrough could have helped add round 23 years to the typical human lifespan.
However this unbelievable progress is now underneath risk. Antibiotic resistance (when micro organism evolve to develop into proof against sure medication) is pushing again in opposition to trendy medication. At present, round a million individuals die every year on account of antibiotic-resistant infections. With out intervention, a 2024 report warned that greater than 39 million individuals might die by 2050 as a result of antibiotic resistance. The World Well being group has even referred to as antibiotic resistance, and extra broadly antimicrobial resistance, “the following pandemic.”
 Pexels
Pexels
It’s a bleak image, however progress is being made. Scientists are starting to raised perceive the place antibiotic resistance comes from. Overprescription is a significant component, as is the widespread use of antibiotics in industrial animal agriculture.
After which there’s plumbing. Sure, the pipes. Particularly, the techniques that carry waste from individuals taking antibiotics into the encompassing water provide.
Analysis has discovered antibiotic-resistant micro organism in pure waterways close to hospitals, the place giant numbers of sufferers are taking medicines. Waste from pharmaceutical producers, healthcare amenities, and even family wastewater additionally permits antibiotics to enter rivers and streams, serving to to create environments the place resistant micro organism can thrive.
 Pexels
Pexels
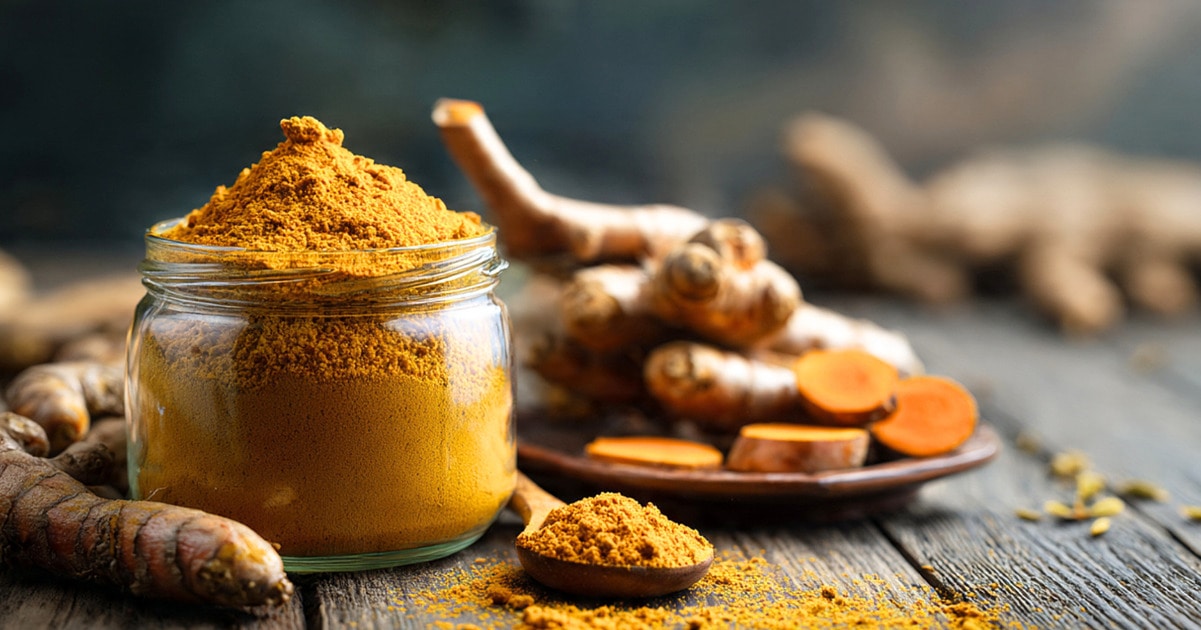
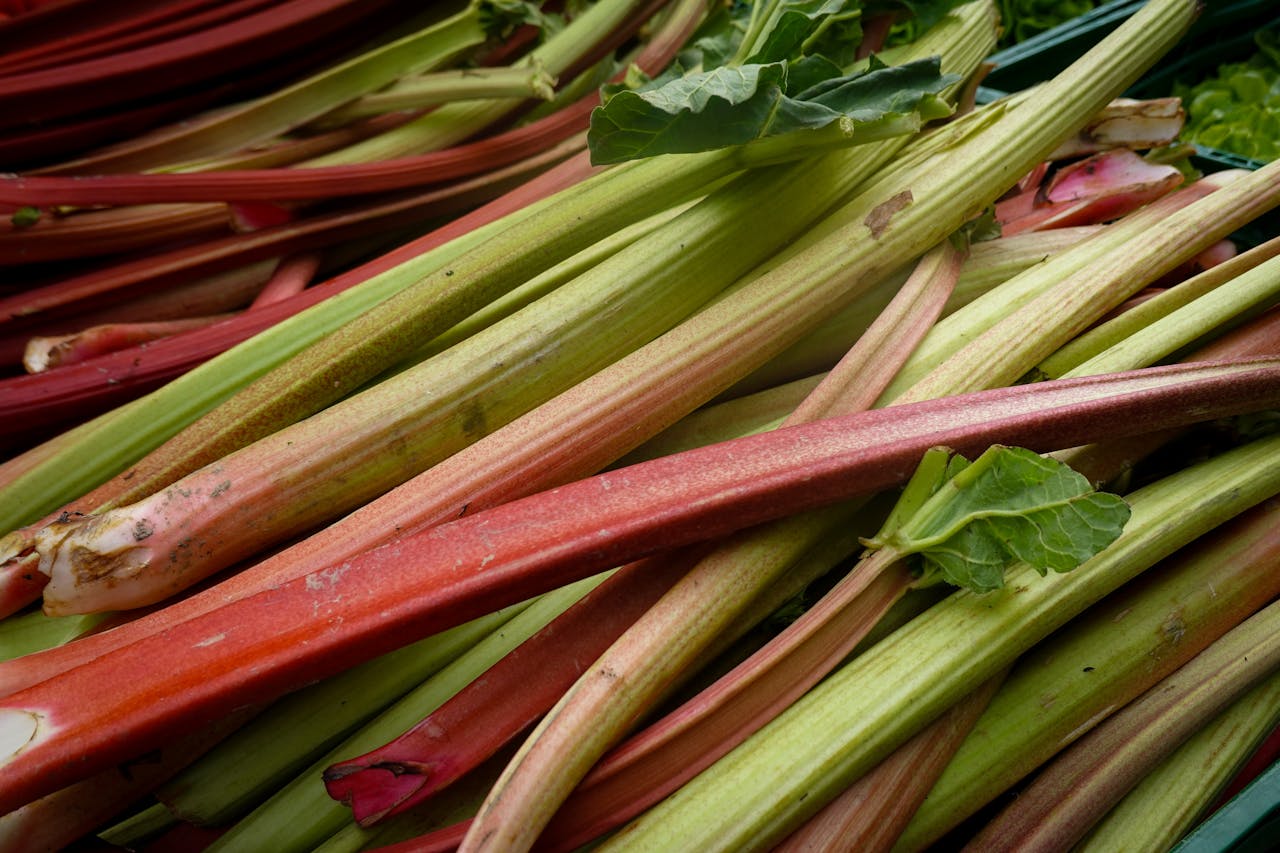
So, how can we deal with the issue? In keeping with a 2025 examine revealed in Frontiers in Microbiology, the reply may be nearer to residence than anticipated. It might lie in two acquainted family components: rhubarb and turmeric.
Why family components might assist deal with antibiotic resistance
Final 12 months, researchers collected wastewater samples, remoted antibiotic-resistant micro organism, and screened them in opposition to 11 completely different plant compounds. They discovered that curcumin from turmeric and emodin from rhubarb appeared to be the best at stopping the expansion of drug-resistant micro organism.
“These compounds have been chosen primarily based on their reported antimicrobial or anti-biofilm properties in earlier research and their pure abundance, making them promising candidates for exploring new, environmentally pleasant approaches to mitigate resistance,” defined lead creator Liyuan (Joanna) Hou, PhD, an environmental microbiologist at Utah State College.
Additional analysis is required to find out whether or not these compounds might assist deal with antibiotic resistance in people or be efficient in real-world wastewater techniques past laboratory situations, however the findings signify a promising begin.
“Future work ought to embrace testing these compounds in complicated wastewater matrices, exploring synergistic results with present therapy processes, and assessing long-term impacts on microbial communities and resistance dynamics,” mentioned Hou. “Moreover, scaling up from laboratory research to pilot-scale trials can be essential for evaluating feasibility and environmental security.”
Within the meantime, there are many different causes so as to add extra turmeric and rhubarb to your weight loss plan. Turmeric is wealthy in antioxidants and is thought to have ant-inflammatory properties, whereas rhubarb is an efficient supply of fiber. Discover out extra in our information to cooking with turmeric right here, and our rhubarb recipe roundup right here.
For extra plant-based tales like this, learn:


